Positioning of Patient
Positioning of Patient in Surgical Operation
§ A proper and careful correct positioning of patient is very important for operation.
It is essential to:
· To maintain proper body alignment, circulatory and respiratory functions.
· For patient safety.
· It allows anesthesia person to monitor airway, administer anesthetic drugs and I/V fluids.
· It protects the patient from nerve injury, protects from circulatory collapse/ shock.
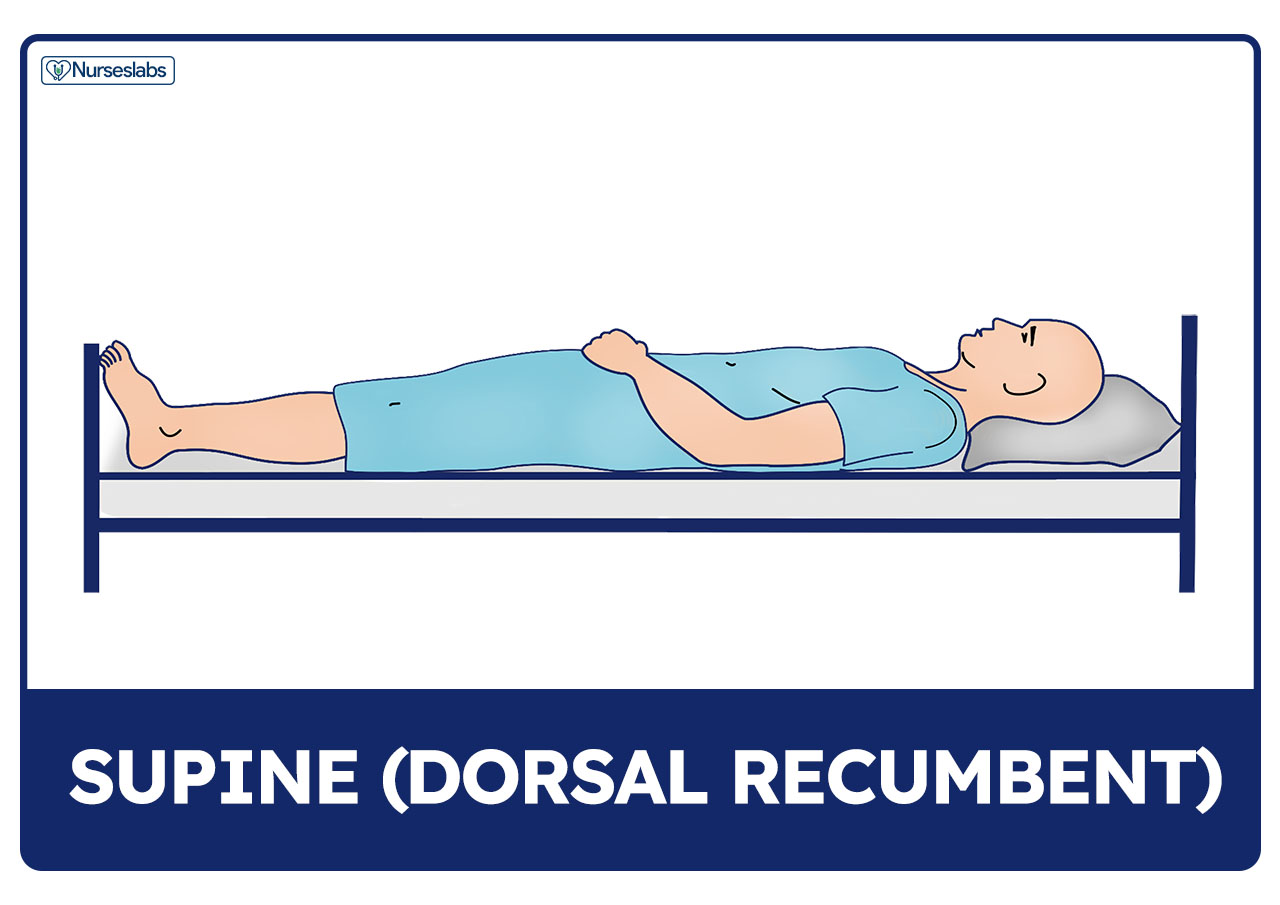
1) Supine or
Dorsal Recumbent position
2)
Trendelenburg (Head Down position)
3) Gall
bladder and liver position
4) Lithotomy
position
5) Breast and
axilla position
6) Neck
position
7) Supine Hip
position
8) Lateral
position f extension
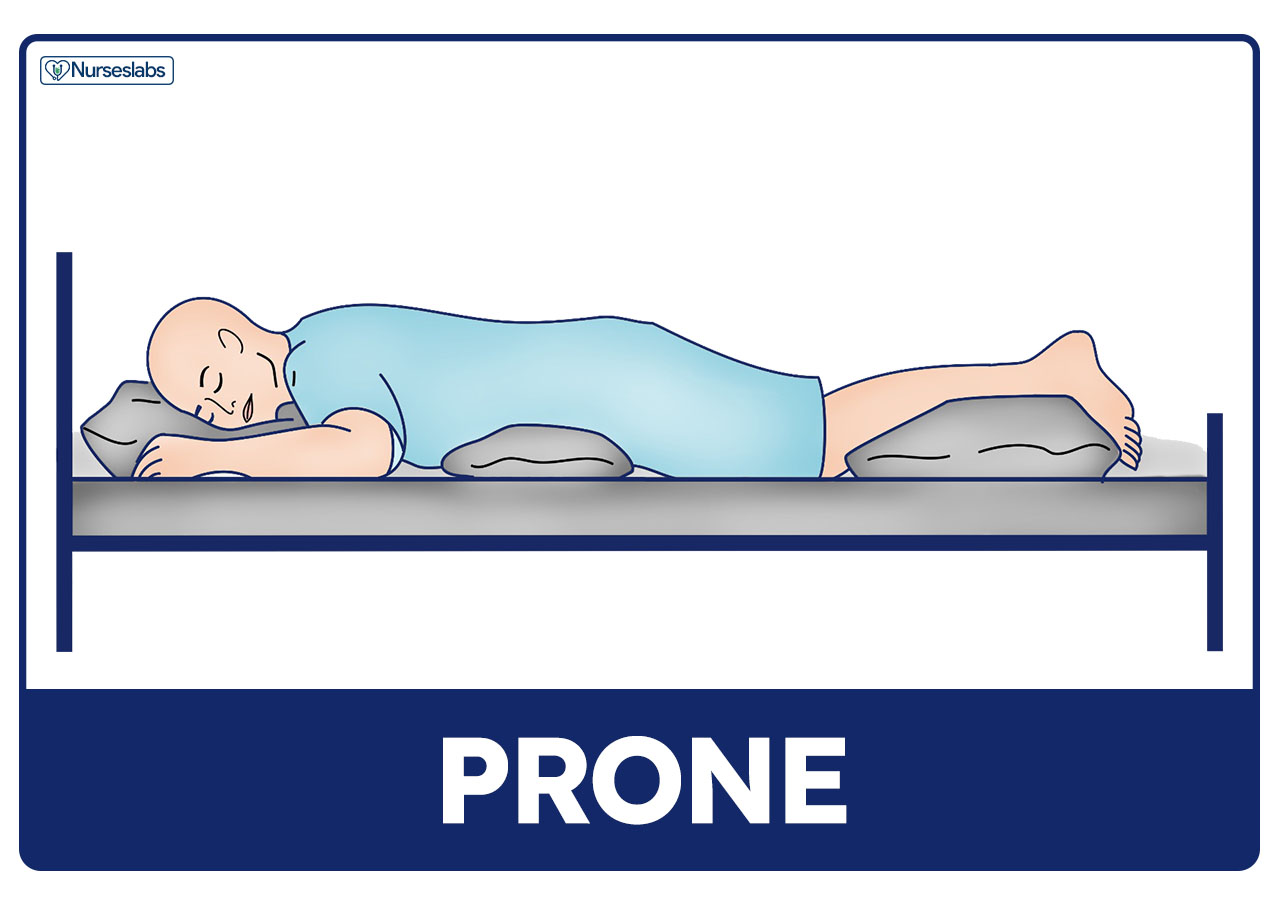
9) Prone
cranial position
10) Sitting cranial
position.
1) Supine or Dorsal Recumbent position
2) Trendelenburg Position (Head Down Position)
§ Disadvantages= decrease BP, risk of Brachial plexus damage.
3) Reverse Trendelenburg Position:
§ It is opposite of Trendelenburg
position.
§The patient lies flat on the
back with table tilted upwards.
§ In this position, the bed
is tilted upwards so that the patient head is higher than the feet.
Uses=It is used for procedures
on head, neck, upper abdomen.
§ This is another modified supine
position.
§ It is used for operations
on gall bladder and liver.
§ The patient is positioned
over the back elevator which is raised to produce extension, and thereby push
the gall bladder towards the anterior abdominal wall.
5) Lithotomy Position ( Leg- up Position)
§ The buttocks project over the edge of the table and
the junction of the centre and foot section which is lowered or removes. The
legs are flexed at the hips and knees, and raised with the feet supported in
webbling slings suspended from the lithotomy poles.
6) Breast and Axilla Position
§ It is used for the
operations on the breast and axilla.
§ It is modifies supine
position, either with both arms extended and secured on arm tables, or one arm
secured by the side of the patient and other on the affected side abducted and
supported by nurse.
7) Neck Extension Position
§ This position is used for
operations on the neck, especially thyroidectomy and tracheostomy.
§ The patient is placed in
the supine position with a pillow or sandbag under the shoulder blades, and the
head is held by a nurse or assistant with the neck well extended; a padded
horse-shoe provides a good support from the head in such operations.
8) Supine Hip Position
§ This is mainly used for nailing
a femoral neck fracture but is also suitable for osteotomy, slipped femoral epiphysis
etc.
§ The patient is in supine
position, with his pelvis supported by a supplementary table top which is translucent
to X-rays and incorporates a slot for introducing anterior position film
cassettes under the pelvis.
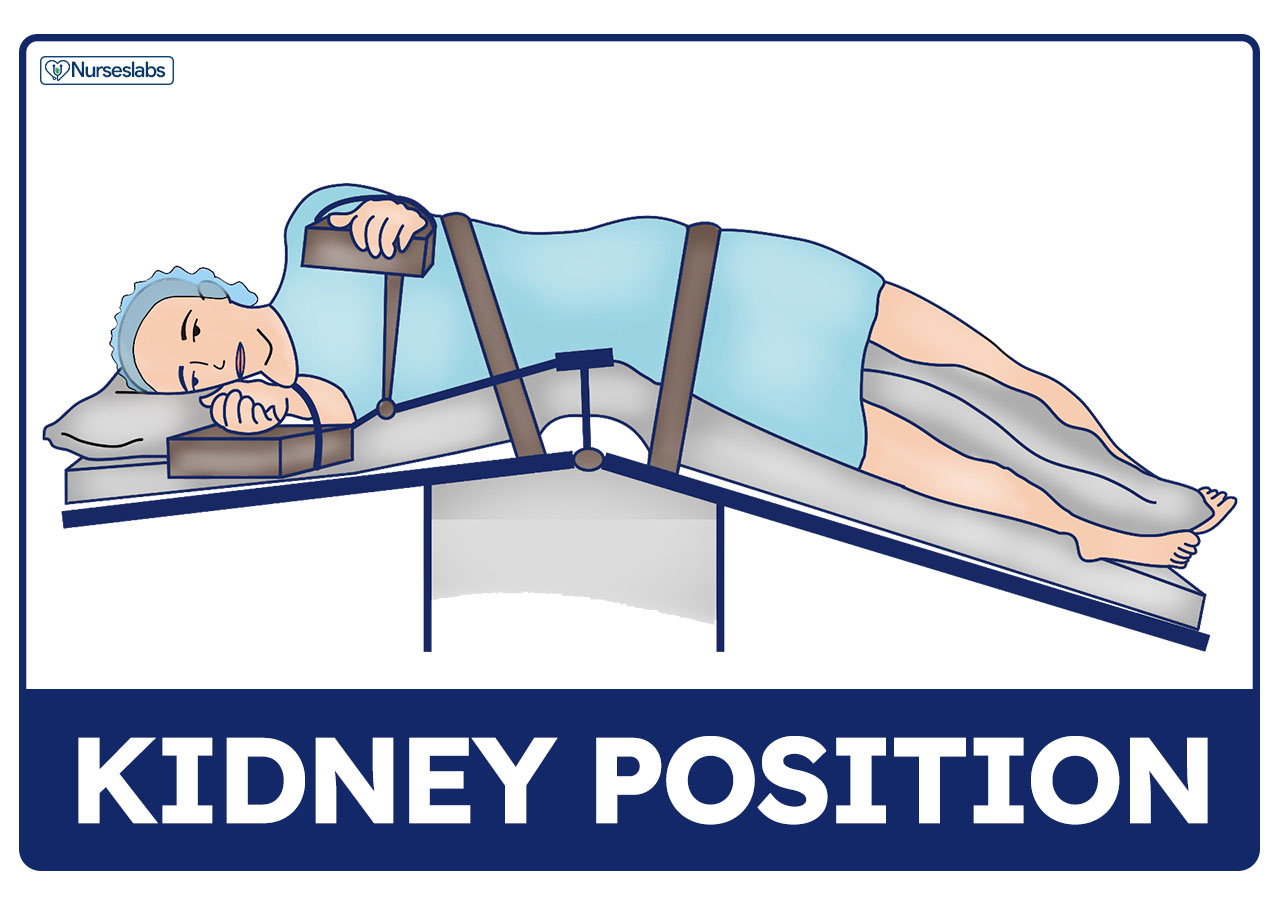
9) Lateral Position of Extension (Kidney Position)
§This is used for operations
on the kidneys, hips and chest but may be modified slightly for operations on
hips.
§ Patient is positioned over
the kidney bridge which is raised to extend this region.
9) Prone Cranial Position
§ This position is used for cerebellar
operations and high cervical laminectomy.
10) Sitting Cranial Position
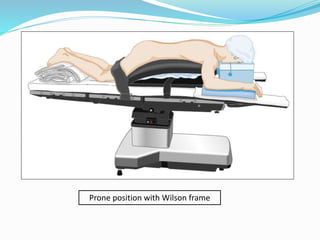
11) Prone Position
§ Patient is lying on the abdomen with rolls or padded frames to allow the diaphragm to move freely and permit the lungs to expand, the arms are positioned either on the patient’s side or on the padded arm board with arms extended outwards and upwards.
12) Genu-Pectoral Position/Knee Chest Position
§ Patient lies with chest
downward on pillow while thigh and knees are flexed with buttock high up in
air.
§ Uses: it is used for vaginal,
cervix and rectal examinations.
§ It is used for introduction
of proctoscope and sigmoisoscope.
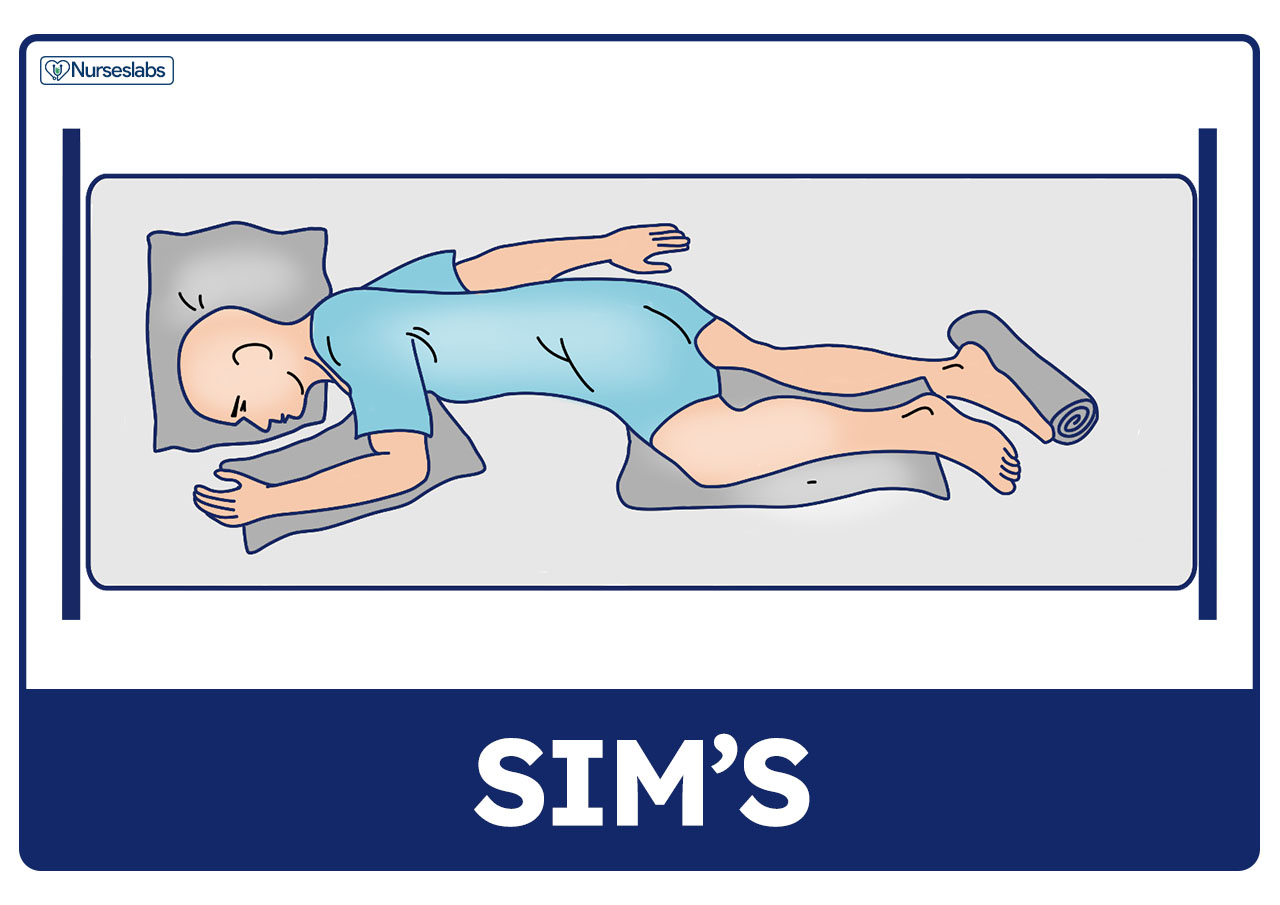
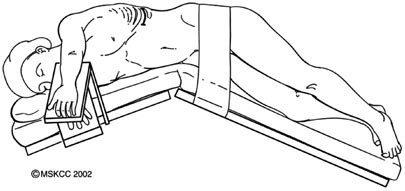
13) Sim’s Position
§ It is same as prone position but patient lies more prone, chest and head resting on one pillow, left arm lying behind back or hanging over edge of bed or table, both knees drawn up, more flexed than left.
§Uses: Vaginal examination
14) Left lateral Position
§ Patient lies on left side, buttocks to edge of bed, head forward on one pillow, thigh and knees flexed.
§ Uses: it is used for Rectal, vaginal and perineal examinations, giving enema and suppositories.
15) Surgical position for Nephrectomy:








.jpg)


-36.jpg)
Comments
Post a Comment